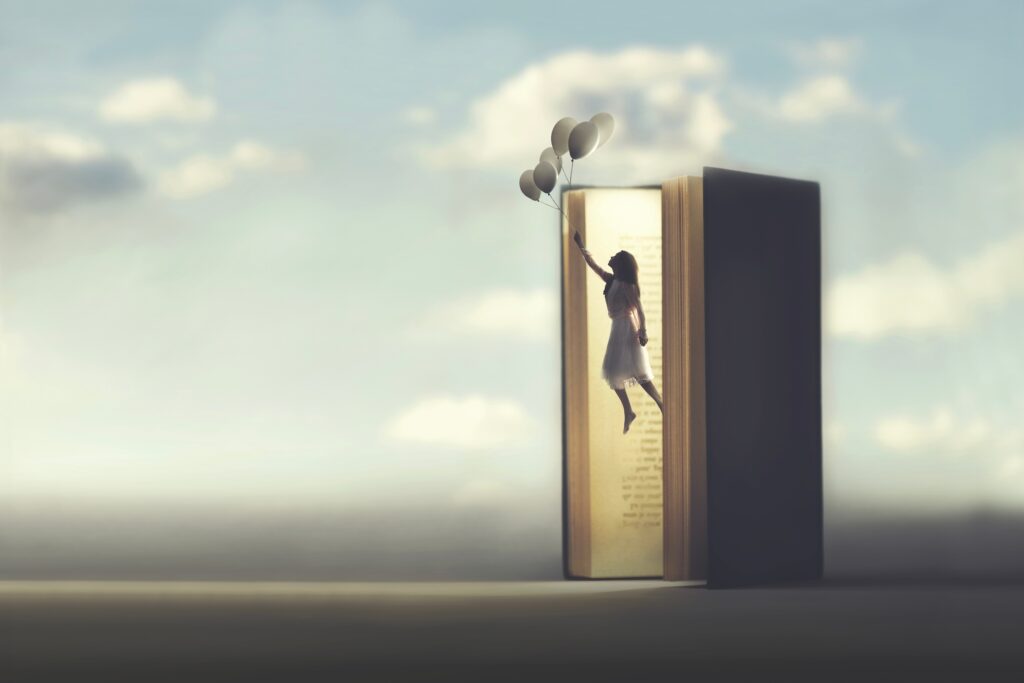
Reconciling the dancing polarities
Reading | Philosophy
![]() Fred Matser | 2023-12-17
Fred Matser | 2023-12-17

In an essay meant to give us food for meditation during the holiday period, as we take account of the year now behind us and the—tragic and otherwise—events that marked the year, our Founder and Chairman speaks to the importance of maintaining, in a mature fashion, the dynamic balance between the often extreme polarities that characterize human society.
In holding polarities apart, resistance creates continuous tension between opposites. By ‘tension’ I don’t mean something negative, but simply a force, a pull. In our case, we can think of this tension as the impetus underlying the interplay between (a) male and female modes of being, (b) intellectual and intuitive modes of cognition, (c) the felt urges to give and receive, (d) the raw power of assertiveness and the enchanting power of vulnerability, and many other polarities. Our very lives rest on the dynamic tension between these opposites being maintained, for without such tension we would live in a world of static aloofness. The tension is the driving force of both people and societies; it is what makes them move, even strive; it is the impetus behind every action, individual or collective; it is the engine of both personal and social growth, authentic growth.
Therefore, the secret to a healthy and functional life, as well as to a healthy and functional society, lies—it seems to me—in ensuring a dynamic harmony between the polarities, whereby neither pole dominates, subdues or overwhelms its opposite but, instead, the tension between them is maintained. This dynamic harmony can be best visualized as a dance performed by each pair of opposites. The better the dance is—that is, the more refined the balance and harmony of the choreography—the more functional is the result. The dance of the polarities isn’t meant to achieve a certain goal or arrive at a particular destination, just as two people dancing a tango aren’t trying to arrive at a specific place on the dance floor. The point is the dance itself, just as the point of sailing is to sail, not to go around buoys.
To grasp the value of life from this perspective requires a certain sense of aesthetics. As Plato suggested, beauty is truth. The most truthful, functional way of life is thus the one that entails the most beautiful dance, the most exquisite choreography. And no tango is beautiful if one of the partners is dominated or stomped into oblivion by the other, is it?
Yet, subduing one of the poles for the benefit of the other has been, consistently, throughout our history, the way we operate. Most conspicuously, we have put physical, assertive power on a pedestal, while neglecting the indispensable role of vulnerability in life, which we see as a weakness. But without the enchanting power of vulnerability life would be impossible. Think of all unborn and newborn animal life, insect larvae, fish fry, plant seedlings, etc.: how vulnerable, yet indispensable, they all are! To use assertive power is perfectly okay as long as it is dynamically balanced with the power of vulnerability, so as to maintain functional tension. Alas, even a cursory observation of our social dynamics reveals that we are far from achieving such an ideal.
There are many more examples of imbalance. Take, for instance, how we value the intellect much above feeling and intuition, as if only the intellect could convey valid information and arrive at valid conclusions. Already since early education, this bizarre and skewed notion is inculcated in children: whatever you know through feeling or intuition is only acceptable if you can persuasively argue for, or justify, it in conceptual terms, using words and numbers. Otherwise, it’s just fantasy, delusion, wishful thinking. Such devaluation of our feeling faculty amounts to a veritable amputation. It artificially and arbitrarily cuts us off from capabilities nature has endowed us with for a reason. It’s like voluntarily gouging out an eye and believing we are better off for it. Because the amputation is not as immediately visible as a missing limb or eye, we don’t realize the magnitude of our loss.
Moreover, the intellect expresses itself innately through discrimination: it is always attempting to draw a line between true and false, right and wrong, valid and invalid, appropriate and inappropriate, belonging and not belonging, etc. Choices made through intellectual mediation are thus intrinsically exclusionary: they exclude what we judge to be false, wrong, invalid, inappropriate or not belonging. In contrast, choices mediated by the feeling faculty—heart-based choices— tend to be inclusionary, to draw things and people together based on their unique strengths and relative value. Consequently, our tendency to value the intellect much above the feeling faculty leads to the myriad ways in which our society excludes people, communities, countries, animals and even nature at large.
One of the most recognized imbalances in our society and way of life is that between male and female modes of thinking, feeling and acting. Therefore, correcting this particular imbalance also gets most of our attention and effort. The problem is that, even in contexts or situations wherein women have managed to break through the glass ceiling and achieve positions of influence, the price they pay for doing so is often to sacrifice their very femininity by imitating the dysfunctional behavior of men. This is too high a price, for it defeats the very purpose of the effort to reduce the imbalance in the first place. Indeed, the detrimental imbalance here is not merely a question of gender, but of modes of being and acting.
If our society embodied a proper dynamic balance between male and female modes of being—regardless of gender—we would arguably be seeing less dysfunctional competition, less wars, less loneliness, more understanding, more sharing and compassion. There is much to be gained by working towards a dynamic balance.
But in order to do so, we must be prepared to revise our values. Balance can only be achieved if each pole is valued on its own terms, not in terms of the qualities of its opposite. This is a subtle but crucial point. For instance, male business leaders who sincerely want to contribute to a better balance between male and female principles at work may still value the intellect and assertive power above intuition and vulnerability; and so, they will support and promote women who think and act like men. At the end, no balance is achieved.
Proper dynamic balance requires a kind of cognitive leap that enables one to contemplate each pole from an Archimedean vantage point; a neutral perspective from which one can objectively assess the polarities within their total context, recognizing their respective contributions to the whole. It is extraordinarily difficult to attain such a neutral vantage point, for we are all immersed in the values we happen to embody. Yet, attaining it is essential if we are to live harmonious, functional lives. This is the key challenge at hand, and it is formidable.

Essentia Foundation communicates, in an accessible but rigorous manner, the latest results in science and philosophy that point to the mental nature of reality. We are committed to strict, academic-level curation of the material we publish.
Recently published
Reading
Essays
Seeing
Videos
Let us build the future of our culture together
Essentia Foundation is a registered non-profit committed to making its content as accessible as possible. Therefore, we depend on contributions from people like you to continue to do our work. There are many ways to contribute.