The dark side of therapy
Reading | Psychiatry | 2022-12-18
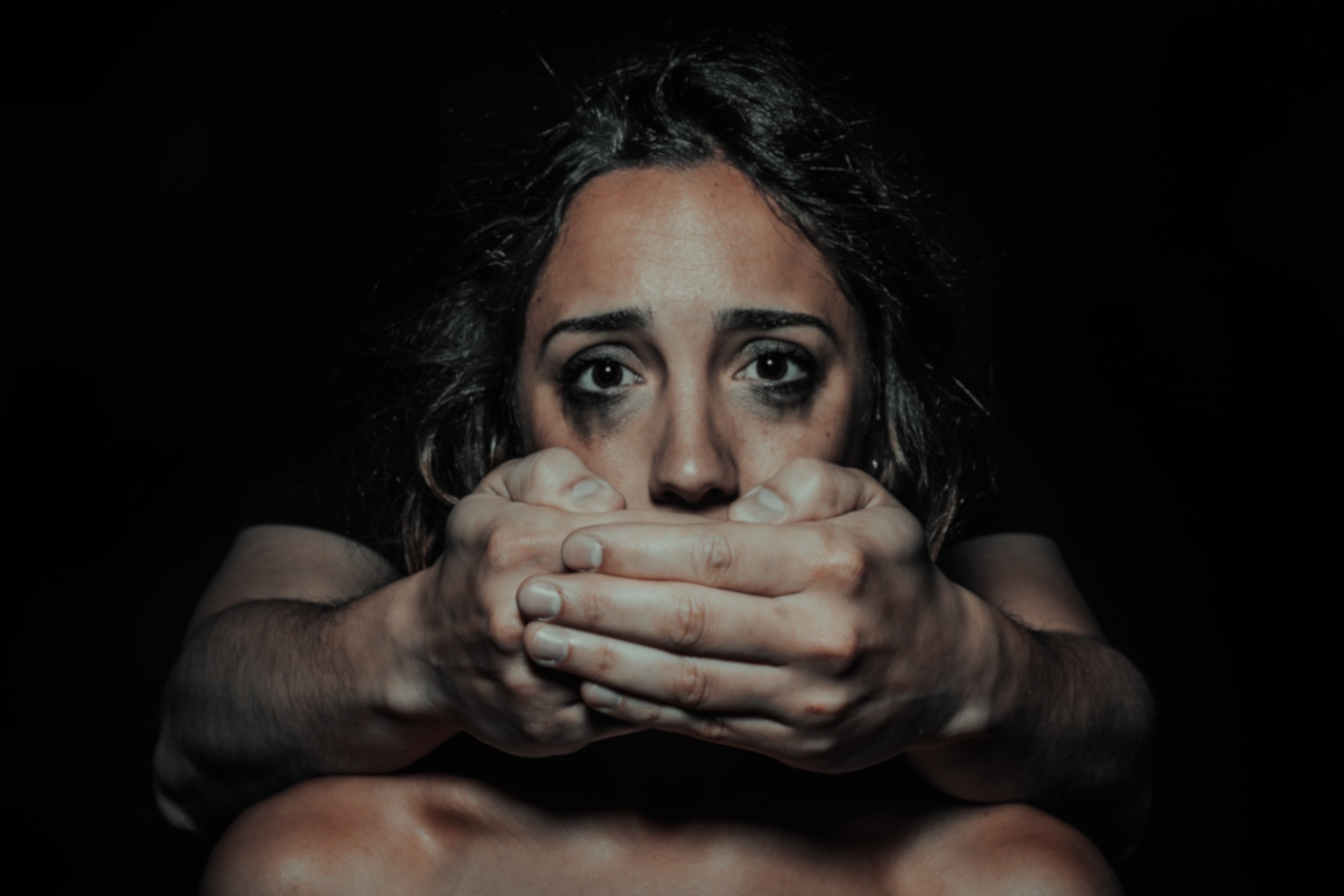

The mental health professions may often play the role of enforcing social norms and conventions, as opposed—or in addition—to being methods for understanding and improving our mental lives, argue the authors. Essentia Foundation believes strongly in the scientific and clinical validity, as well as the critical importance, of psychology and psychiatry in reducing suffering in our society. As such, we may hold a different view than that of the authors. Nonetheless, we find this essay well argued and well documented, and believe it does offer thoughtful, valid points even to those who, like us, defend the validity and importance of the mental health professions.
Nowadays, ‘go to therapy’ has become the progressive phrase in our society to deal with any issue that anyone has. If you are feeling sad, you are told to go to therapy, maybe even in place of some condolences. If you are feeling nothing and empty, of course that’s where you should go. Even if you are feeling too happy, anything shorter than going to therapy will be met with ‘Why aren’t you going to therapy?’
Many people presuppose psychology and psychiatry are scientifically objective, special bodies of truth tailored to help you succeed in life. Why wouldn’t you trust them? However, their history might reveal that they’re not best cataloged as branches of science, but a branch of law.
Imagine the following thought experiment. There is a Medieval slave working in the fields. Everyday, if he doesn’t accomplish the unreasonable goals set by his master, he’ll be harshly whipped. One might expect the slave to become upset and work less over time. The master, analyzing the situation, decides to send his slave to the town therapist. In the middle of the session, as the slave lays on the couch, he begins to cry his heart out and explain his deeply rooted traumas. While his therapist adjusts his glasses, he uses the latest Logotherapy techniques to get the slave to heal emotionally. The slave, after experiencing profound relief, says thank you to the therapist, goes back to his field, and is now able to meet the demands of his master with a smile on his face.
In the Medieval Ages, kings were anointed by God himself. Subsequently, the order established by the king was of a divine nature, or the truth itself. But with scientific discourse gaining traction during the Enlightenment, the exertion of power could no longer be justified using God. Needing a new way to validate the law, religion was left behind, and criminology, psychiatry, psychology, and sociology were born to take its place [1].
Law only works if people follow it. An easy way to correct dissension from the law is to statistically prove that those who do not follow it are ‘abnormal.’ Therefore, in this new paradigm, we can see the act of measuring increasingly affecting the lives of the citizens. It became more common to collect information about individuals, in different institutions such as schools, banks, factories, hospitals, the army, and others. Those who conformed to the rules were rewarded, and those who did not were punished [1]. If you were a statistical anomaly, you might be labeled as ‘mentally ill.’
The Soviet Union used this technique to justify punishing those who spoke out against their political system. The subversive people were labeled “Sluggish Schizophrenics,” and the purported symptoms included: “perseverance,” “struggling for the truth,” and “delusions of political reform” [3]. These ‘patients’ were forcibly sent to correctional facilities, and were treated with strong doses of antipsychotic medication [6]. China had its own equivalent to stop political dissenters, preferring the terms “paranoia” or “paranoid schizophrenia.” Chinese citizens who were deemed “politically harmful for society” for similar reasons as the Soviets could face abuse, torture, and strong doses of neuroleptics [2]. China continuously uses this technique to keep its social order running [7]. Additionally, psychiatry was used to justify the American slave trade. In 1851, the physician Samuel Cartwrite decided a slave must be mentally insane to want to run away from the “pleasant life” of captivity. He called it “Drapetomania,” and recommended treatment by intense whipping and cutting off the slaves’ toes to make it physically harder to run away [4].
Nowadays, many people think of mental illnesses as something completely inside themselves. We might only point to our neurobiology for our depression, anxiety, or ADHD, referencing “chemical imbalances” or thinking of the neurons as somehow “misfiring” in a vacuum. However, adopting this reductionist viewpoint could lead us to ignore the social influences in every aspect of our lives. If you were to look at the brains of “Sluggish Schizophrenics,” you would probably find a difference from others in the population. Does that necessarily mean that they’re ill? In order to get a clearer sight of the situation, we would need to look at all of the factors at our disposal, and break down the epistemology that is leading us to our conclusions.
It is no measure of health to be well adjusted to a profoundly sick society.
Jiddu Krishnamurti. [8]
Some academics seem to be pushing towards renaming “mental illness” as “brain disease.” This implies to some degree that we should be putting all of our efforts in the individual ‘brains’ that hold these problems, again adopting a reductionist stance [5].
According to Dr. Laurence J. Kirmayer, different cultures create different “valid” manifestations of discontent, which are perceived as legitimate in their societies. For example, in Nigeria, depression is more likely to be reported as “a peppery feeling in [the] head” than in India, where depression is experienced as “semen loss or a sinking heart or feeling hot.” In Korea, depression might be defined as “fire illness” due to a burning sensation in the gut, while it might be marked as “tightness in the chest” in Iran.
These differences are not inconsequential, and are associated with examples of social maladies more than neurological maladies. In the US, depression is characterized by certain particular symptoms, such as isolation. For a Korean, depression is associated with “a collective experience of injustice” [9].
Today, precarious social conditions might lead us to a certain angst that pushes us to find a label for it, something to identify ourselves with. Psychiatry and psychology seem to provide this. However, we might be sustaining the very conditions that gave birth to this pain in the first place. We might find that many of those conditions would be of a political and/or legal nature. Psychiatry and psychology could be driving forces to create positive changes in society, but instead they seem to frequently be a way to create individualized guilt and conform to the laws that keep the systematic problems in place.
Citations
[1] Foucault, Michel. (2020). La Verdad y las formas juridicas. GEDISA EDITORIAL.
[2] Google. (n.d.). On dissidents and madness. Google Books. Retrieved March 13, 2022, from https://books.google.com/books?id=tyDIKu8XsgcC&pg=PA242#v=onepage&q=paranoid&f=false
[3] Graber, M. G., Weiner, A., & Mason, D. (n.d.). Sluggish schizophrenia in the Soviet Union: A diagnosis for political dissenters. in SearchWorks catalog. Retrieved March 13, 2022, from https://searchworks.stanford.edu/view/cj200yf2075
[4] Haley, A. (n.d.). Trauma of Slavery: A Critical Study of the Roots. cloudfront.net. Retrieved March 13, 2022.
[5] JD;, B. (n.d.). Mental illness and brain disease. Folia medica. Retrieved March 13, 2022, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26444362/
[6] States., U. (n.d.). Psychiatric abuse of political prisoners in the Soviet Union : Testimony by Leonid Plyushch : Hearing before the Subcommittee on International Organizations … HathiTrust. Retrieved March 13, 2022, from https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=pur1.32754076920721&view=1up&seq=1&q1=treatment
[7] van Voren, R. (2010, January). Political abuse of psychiatry—an historical overview. Schizophrenia bulletin. Retrieved March 13, 2022, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2800147/
[8] Vonnegut, M. (n.d.). The Eden Express. Google Books. Retrieved March 13, 2022, from https://books.google.com/books?id=o89v2m2ybCEC&q=%22well-adjusted%2Bto%2Ba%2Bprofoundly%2Bsick%2Bsociety%22
[9] Watters, E. (2011). Crazy like us: The globalization of the American psyche. Free Press.

Essentia Foundation communicates, in an accessible but rigorous manner, the latest results in science and philosophy that point to the mental nature of reality. We are committed to strict, academic-level curation of the material we publish.
Recently published
Reading
Essays
Seeing
Videos
Let us build the future of our culture together
Essentia Foundation is a registered non-profit committed to making its content as accessible as possible. Therefore, we depend on contributions from people like you to continue to do our work. There are many ways to contribute.